A monument not only of stone and mortar but of human determination and endurance, the Castillo de San Marcos symbolizes the clash between cultures which ultimately resulted in our uniquely unified nation. Still resonant with the struggles of an earlier time, these original walls provide tangible evidence of America’s grim but remarkable history.

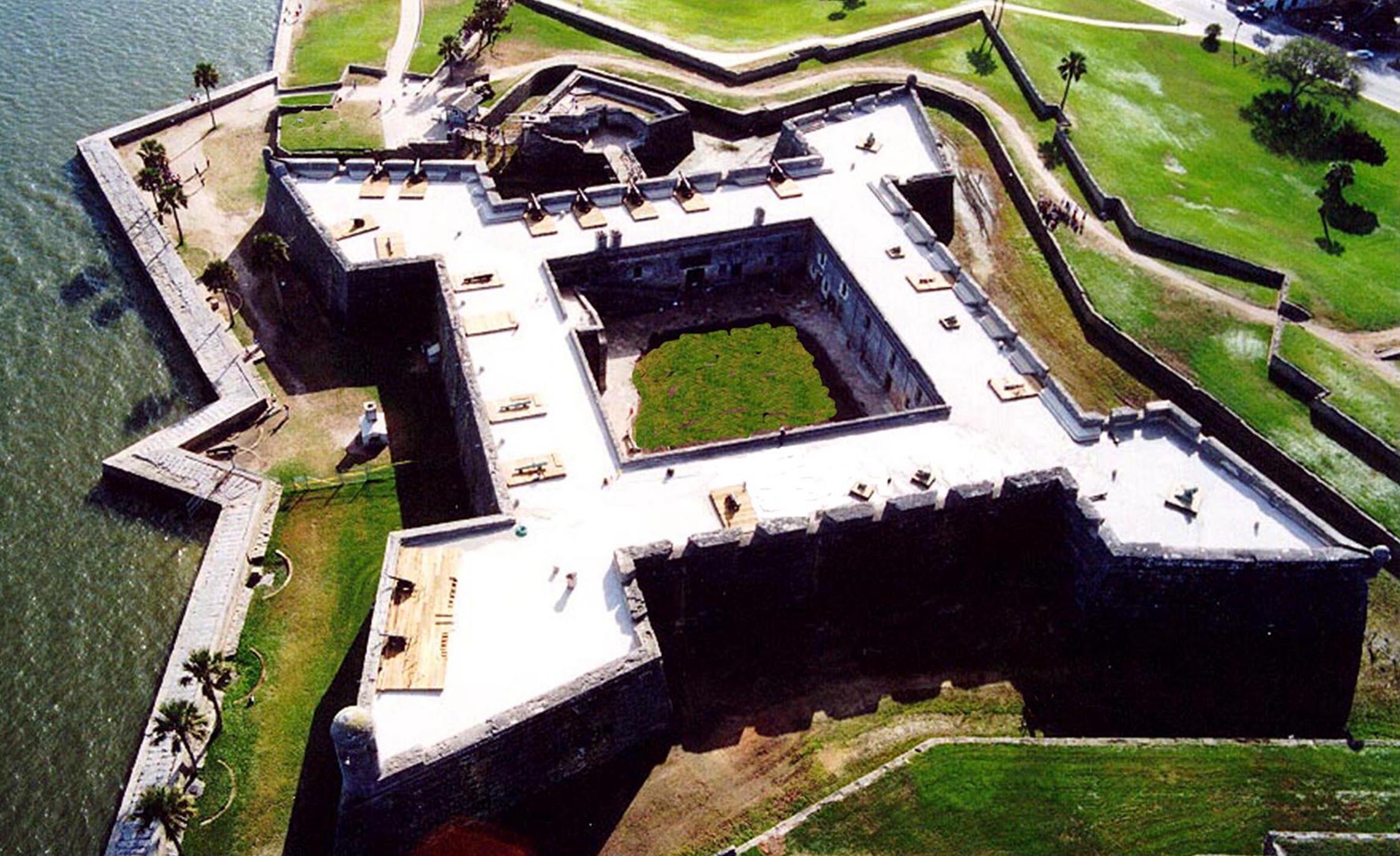
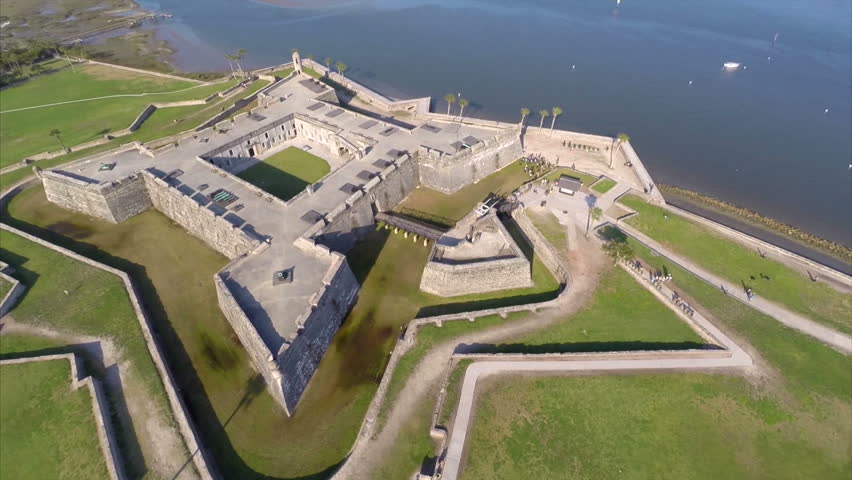
The Castillo de San Marcos is the oldest and largest masonry fort in the continental United States; it is located on the western shore of Matanzas Bay in the city of St. Augustine, Florida. The Castillo was designed by the Spanish engineer Ignacio Daza, with construction beginning in 1672, 107 years after the city's founding by Spanish Admiral and conquistador Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, when Florida was part of the Spanish Empire. The fort's construction was ordered by Governor Francisco de la Guerra y de la Vega after a raid by the English privateer Robert Searles in 1668 that destroyed much of St. Augustine and damaged the existing wooden fort. Work proceeded under the administration of Guerra's successor, Manuel de Cendoya in 1671, and the first coquina stones were laid in 1672. The construction of the core of the current fortress was completed in 1695, though it would undergo many alterations and renovations over the centuries.

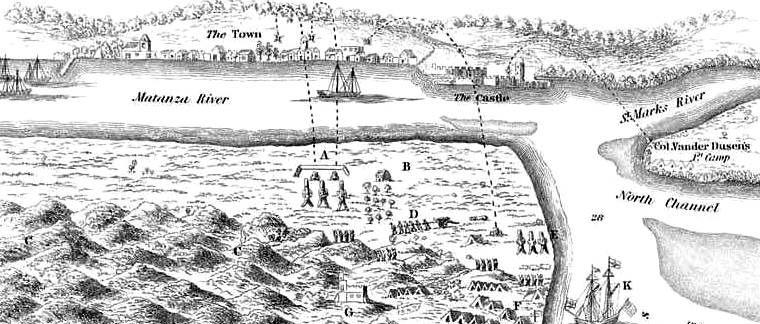
Castillo de San Marcos was attacked several times and twice besieged: first by English colonial forces led by Carolina Colony Governor James Moore in 1702, and then by English Georgia colonial Governor James Oglethorpe in 1740, but was never taken by force. However, possession of the fort has changed six times, all peaceful, among four different governments: Spain, 1695–1763 and 1783–1821, Kingdom of Great Britain, 1763–1783, and the United States of America), 1821–date (during 1861–1865, under control of the Confederate States of America).

Under United States control the fort was used as a military prison to incarcerate members of Native American tribes starting with the Seminole—including the famous war chief, Osceola, in the Second Seminole War—and members of western tribes, including Geronimo's band of Chiricahua Apache. The Native American art form known as Ledger Art had its origins at the fort during the imprisonment of members of the Plains tribes such as Howling Wolf of the southern Cheyenne.
The European city of St. Augustine was founded by the admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés for the Spanish Crown in 1565 on the site of a former Native American village called Seloy. The need for fortifications was recognized after it was attacked by Sir Francis Drake and his fleet of 22 ships in 1586, and over the next 80 years, a succession of nine wooden forts were built in various locations along the coastline. However, after a 1668 attack by the English pirate Robert Searle during which the town of St. Augustine was burned to the ground, wooden forts were deemed inadequate, and Mariana, Queen Regent of Spain, approved the construction of a masonry fortification to protect the city.

The Castillo is a masonry star fort made of a stone called coquina (Spanish for "small shells"), which consists of ancient shells that have bonded together to form a sedimentary rock similar to limestone. Native Americans from Spain's nearby missions did most of the labor, with additional skilled workers brought in from Havana, Cuba. The coquina was quarried from the 'King's Quarry' on Anastasia Island in what is today Anastasia State Park across Matanzas Bay from the Castillo, and ferried across to the construction site. Construction began on October 2, 1672, and lasted twenty-three years, with completion in 1695.

The fort has four bastions named San Pedro, San Agustín, San Carlos and San Pablo with a ravelin protecting the sally port. On the two landward sides a large glacis was constructed which would force any attackers to advance upward toward the fort's cannon and allow the cannon shot to proceed downslope for greater efficiency in hitting multiple targets. Immediately surrounding the fort was a moat which was usually kept dry, but that could be flooded with seawater to a depth of about a foot in case of attack by land.
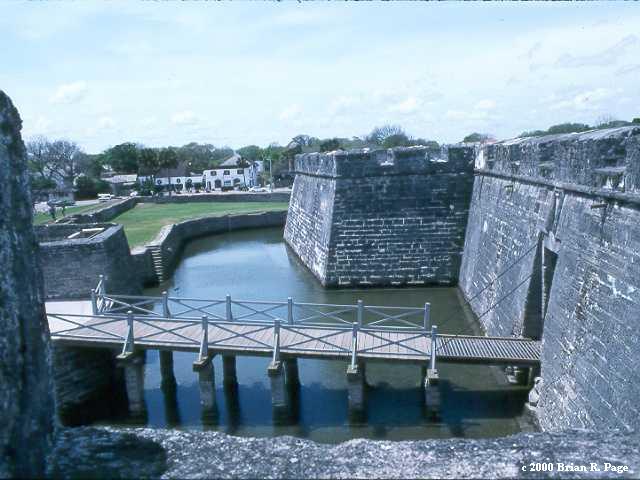

Multiple embrasures were built into the curtain wall along the top of the fort as well as into the bastions for the deployment of a cannon of various calibers. Infantry embrasures were also built into the walls below the level of the terreplein for the deployment of muskets by the fort's defenders. It was through one of these embrasures that twenty Seminoles held as prisoners would escape in 1837.
In 1670, Charles Town (modern-day Charleston, South Carolina) was founded by English colonists. As it was just two days' sail from St. Augustine, the English settlement and encroachment of English traders into Spanish territory spurred the Spanish in their construction of a fort. In 1702, English colonial forces under the command of Carolina Governor James Moore embarked on an expedition to capture St. Augustine early in Queen Anne's War.
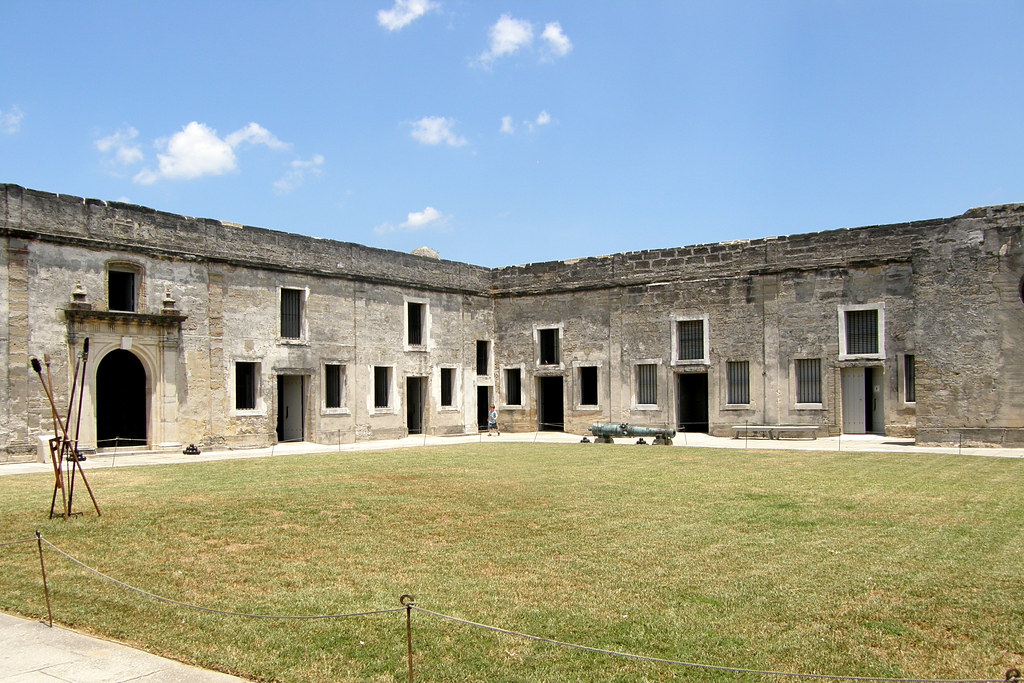
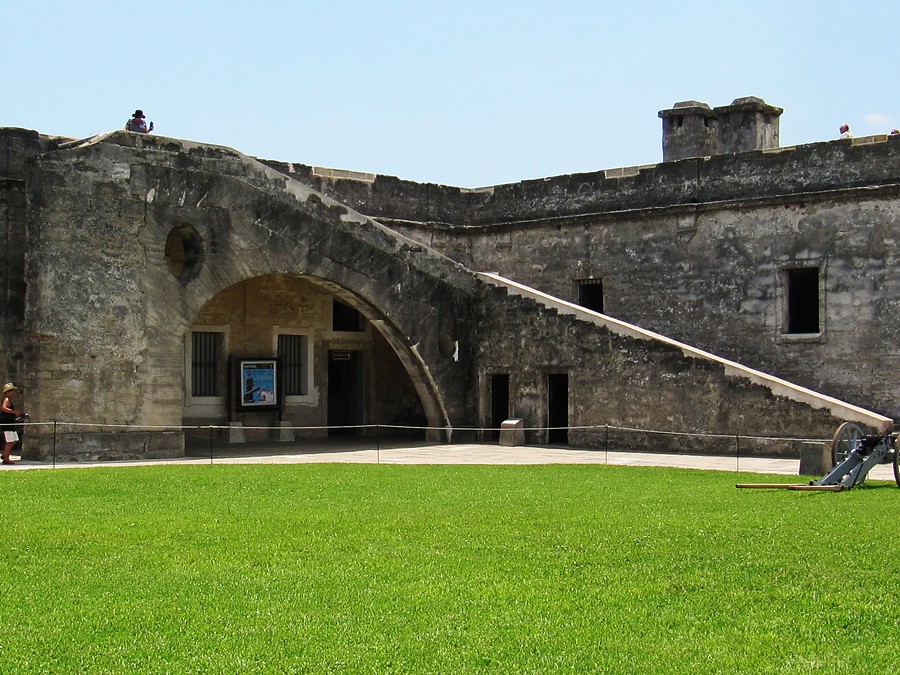
Beginning in 1738, under the supervision of Spanish engineer Pedro Ruiz de Olano, the interior of the fort was redesigned and rebuilt. Interior rooms were made deeper, and vaulted ceilings replaced the original wooden ones. The vaulted ceilings allowed for better protection from bombardments and allowed for cannon to be placed along the gun deck, not just at the corner bastions.
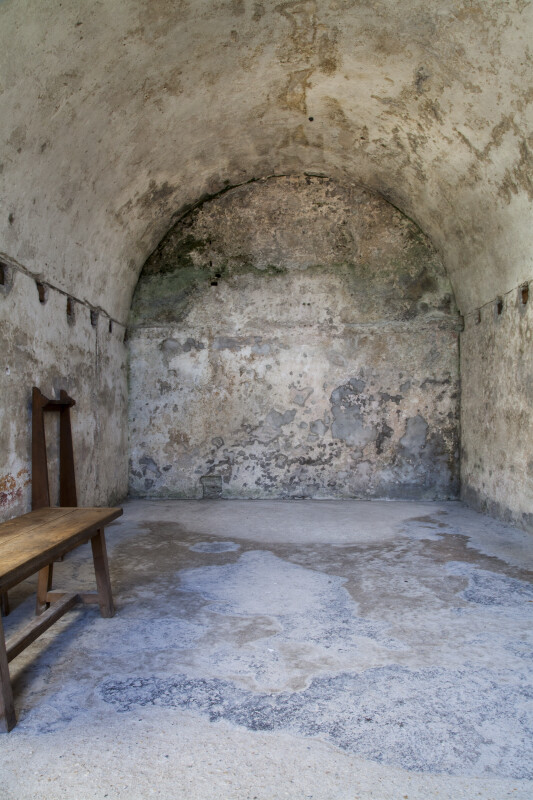

Inner Vaults for Mortars
The new ceilings required the height of the exterior wall to be increased from 26 to 33 feet (10 m). In 1898, over 200 deserters from the Spanish–American War were imprisoned at the fort. This marked one of the last uses of the fort as an operational base. In 1900, the fort was taken off the active duty rolls after 205 years of service under five different flags.

Inner Windows For Lookouts
Then after a long on the period of second United States In 1924, the fort was designated a National Monument. In 1933 it was transferred to the National Park Service from the War Department. In 1942, in honor of its Spanish heritage, Congress authorized renaming the fort as Castillo de San Marcos. As an historic property of the National Park Service, the National Monument was listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) on October 15, 1966. The National Park Service manages the Castillo together with Fort Matanzas National Monument. In 1975, the Castillo was designated a Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers.